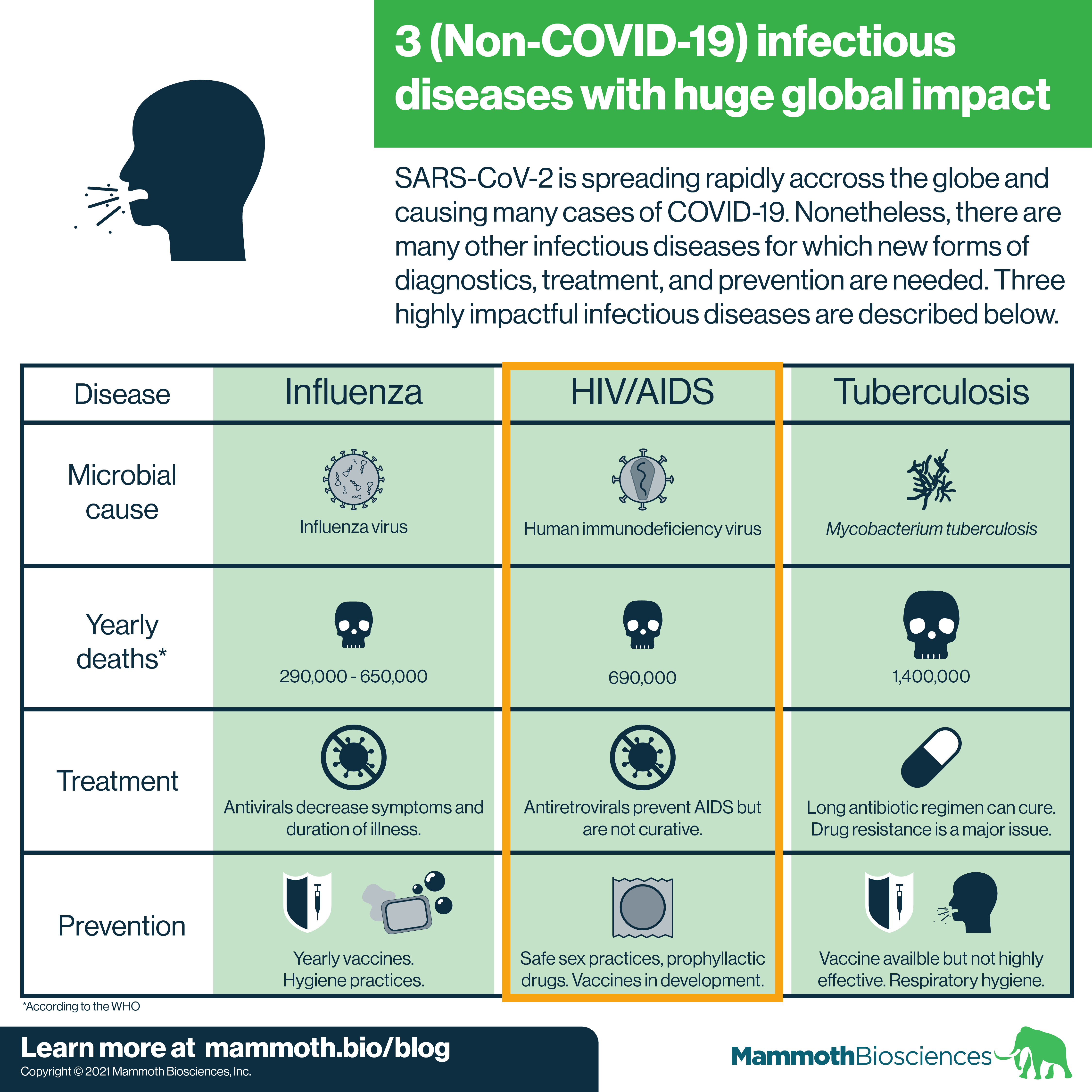
39 hiv and aids are different labels for the same disease
HIV vs. AIDS: What's the Difference? - Healthline AIDS is a condition. While HIV is a virus that may cause an infection, AIDS (which is short for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a condition. Contracting HIV can lead to the development of ... Toxoplasma gondii Encephalitis | NIH - HIV.gov The differential diagnosis of focal neurological disease in patients with AIDS most often includes primary CNS lymphoma and progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy (PML). In the absence of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS), PML (but not lymphoma) can be distinguished on the basis of imaging studies.
History of AIDS - HISTORY In the 1980s and early 1990s, the outbreak of HIV and AIDS swept across the United States and rest of the world, though the disease originated decades earlier. Today, more than 70 million people ...
Hiv and aids are different labels for the same disease
Difference Between AIDS and HIV - Collegedunia HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. HIV causes AIDS, HIV spreads like any other virus and AIDS is a contractable disease. Fatigue, Fever, Severe Headaches, Swollen Lymph nodes are few of the symptoms along with flu-like conditions that mark the HIV infection. AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) | Cedars-Sinai Having been infected with HIV (being HIV positive and having HIV antibodies in the blood) is not the same as having AIDS. Symptoms Persons who are infected with HIV may not know it. Some people experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, muscles and joints, stomachache, swollen lymph glands or a skin rash that lasts one to two weeks. With monkeypox, the world must heed the lessons of HIV/AIDS In fact, if we learned one thing from HIV/AIDS, it's that infectious diseases - even if they are sexually transmitted - never stay confined to one group of people and eventually spread throughout...
Hiv and aids are different labels for the same disease. HIV | CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC provides leadership for HIV prevention research and surveillance and the development and testing of effective biomedical interventions to reduce transmission and HIV disease progression in the United States and internationally. It also provides national leadership in the development, implementation, and evaluation of evidence-based HIV prevention programs serving persons affected by, or at ... HIV Infection and AIDS: Practice Essentials, Background ... - Medscape Practice Essentials. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a blood-borne virus typically transmitted via sexual intercourse, shared intravenous drug paraphernalia, and vertical transmission during the birth process or via human milk. HIV disease is caused by infection with HIV-1 or HIV-2, which are retroviruses in the Retroviridae family ... Solved 2. HIV and AIDS are different labels for the same - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (2 ratings) 2. HIV and AIDS are different labels for the same dis …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 2. HIV and AIDS are different labels for the same disease. O true ő false SUBMIT. HIV/AIDS Symptoms, Stages, & Early Warning Signs - WebMD Early signs of HIV include: Headache. Fatigue. Aching muscles. Sore throat. Swollen lymph nodes. A red rash that doesn't itch, usually on your torso. Fever. Ulcers (sores) in your mouth, esophagus ...
HIV and AIDS: Medicines to Help You | FDA HIV kills these cells. There are medicines that you can take to reduce the amount of HIV and increase the CD4 cells in your body. These medicines do not cure HIV, but can help you live a longer ... Disseminated Mycobacterium avium Complex Disease | NIH - HIV.gov similar to tuberculosis (tb), mac-associated iris can occur as "unmasking" iris in people with hiv with subclinical (undiagnosed) mac or "paradoxical" iris in those with previously established mac disease. 28-32 both variants occur primarily in those with advanced immunosuppression who begin art and have a rapid and marked reduction in plasma hiv … Understanding HIV and AIDS | Be in the KNOW Understanding HIV and AIDS. HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system and leads to AIDS if it isn't treated. Find out more about the virus and how it infects the body. What are HIV and AIDS? How HIV infects the body. HIV symptoms. HIV cure. African Countries Grapple With HIV Patients ... - Health Policy Watch In Tanzania, six hospital sites are starting to integrate diabetes and hypertension into HIV programmes. But Dr Kaushik Ramaiya, CEO of Shree Hindu Mandal Hospital in Tanzania, stressed that, while a lot of money has been invested in HIV, the same was not true for NCDs. "HIV drugs are free, TB drugs are free, but NCD drugs are not free and ...
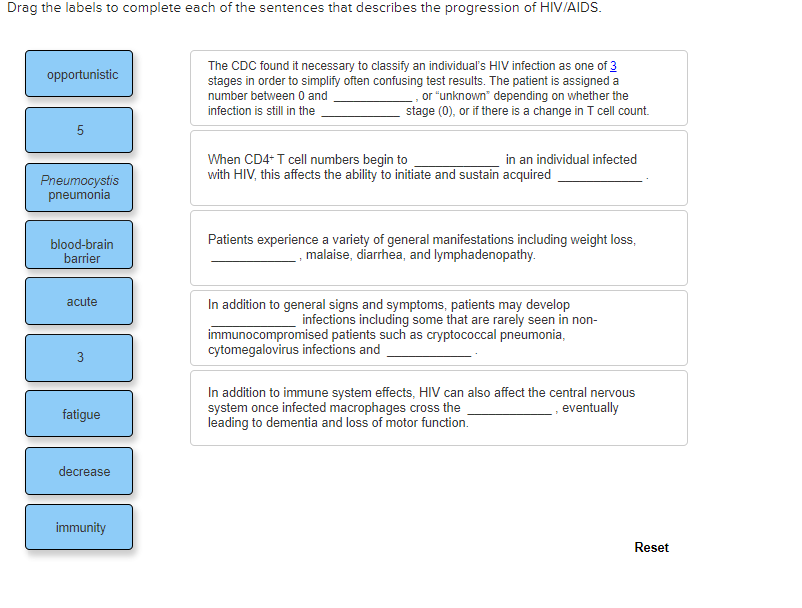
HIV and AIDS: An Origin Story - PublicHealth.org By the end of the year, the first case of HIV's full-blown disease state, Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS), was documented. Featured Online Programs At this point, there was no direct line connecting these early infectious diseases to AIDS. It took researchers several years to fully establish the connection. HIV/AIDS - Wikipedia Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is defined as an HIV infection with either a CD4 + T cell count below 200 cells per µL or the occurrence of specific diseases associated with HIV infection. [30] In the absence of specific treatment, around half of people infected with HIV develop AIDS within ten years. [30] What is the Difference between HIV and AIDS? | STD Check HIV attacks and destroys specific immune system cells called CD4 cells. The body's loss of these cells makes it less able to ward off other diseases and infections, including cancers. AIDS stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. AIDS is the final, most advanced stage of an HIV infection. HIV Testing | NIH - National Institutes of Health HIV testing determines if a person is infected with HIV. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection. HIV testing can detect HIV infection, but it cannot tell how long a person has had HIV or if the person has AIDS.
chapter 10 developmental psyc Flashcards | Quizlet HIV and AIDS are different labels for the same disease. false HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. AIDS is an advanced stage of HIV infection in which the immune system is extremely compromised making the patient very vulnerable to various infections. Adolescent egocentrism helps young people to focus on themselves and practice safe sex. false
The HIV Life Cycle | NIH - National Institutes of Health The seven stages of the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding, 2) fusion, 3) reverse transcription, 4) integration, 5) replication, 6) assembly, and 7) budding. To understand each stage in the HIV life cycle, it helps to first imagine what HIV looks like. Now, follow each stage in the HIV life cycle as HIV attacks a CD4 cell and uses the machinery of ...
Monkeypox in the U.S. - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The signs and symptoms of monkeypox virus infection are similar in people with or without HIV, including characteristic rash, fever, and lymphadenopathy. For immunocompromised people, monkeypox virus infection may present with atypical manifestations or more severe illness (for example, sepsis, disseminated rash).
What are HIV and AIDS? | Be in the KNOW HIV and AIDS are different but connected. HIV is a virus that can get into our bodies and start to make us sick over a period of time. AIDS is a set of symptoms and illnesses that develop at the final stage of HIV infection. HIV can become AIDS if it is not treated. But treatment means you can stay healthy and live a long life without getting AIDS.
List of 109 HIV Infection Medications Compared - Drugs.com The next stage of HIV infection is called clinical latent infection. Generally, there are few signs or symptoms during this stage which may last approximately 10 years, although some people may develop persistent swelling of the lymph nodes or more severe disease sooner. HIV persists in the bloodstream and white blood cells.
HIV & AIDS - What is AIDS? - VirusMyth HIV is a "spectrum" illness: all who are infected have the same disease, but there are many different stages to it. AIDS is the name given only to the most serious stage of HIV disease. In the least serious stage, people are HIV seropositive, meaning they have tested positive on the HIV antibody test but have no symptoms of illness.
History of HIV and AIDS: 1981-2021, Statistics, and More - Healthline The earliest cases of HIV HIV, the virus that can lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), remains one of the largest epidemics in the world today. AIDS was first identified in the United...
The new face of HIV/AIDS in Jacksonville: Rising disease rates strip ... Meanwhile, HIV/AIDS was the third-leading cause of death among black men in that age range, with 170 deaths out of 1,067. In Duval County, for the same demographic group, it was the second-leading...
The HIV Life Cycle—Understanding HIV Replication - Verywell Health Ziagen (abacavir), Sustiva (efavirenz), Viread (tenofovir), and Pifeltro (doravirine) are just some of the reverse transcriptase inhibitors commonly used to treat HIV. 7 Integration In order for HIV to hijack the host cell's genetic machinery, it must integrate the newly formed DNA into the nucleus of the cell.
HIV - Wikipedia The human immunodeficiency viruses ( HIV) are two species of Lentivirus (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), [1] [2] a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. [3]
With monkeypox, the world must heed the lessons of HIV/AIDS In fact, if we learned one thing from HIV/AIDS, it's that infectious diseases - even if they are sexually transmitted - never stay confined to one group of people and eventually spread throughout...
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) | Cedars-Sinai Having been infected with HIV (being HIV positive and having HIV antibodies in the blood) is not the same as having AIDS. Symptoms Persons who are infected with HIV may not know it. Some people experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, muscles and joints, stomachache, swollen lymph glands or a skin rash that lasts one to two weeks.
Difference Between AIDS and HIV - Collegedunia HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. HIV causes AIDS, HIV spreads like any other virus and AIDS is a contractable disease. Fatigue, Fever, Severe Headaches, Swollen Lymph nodes are few of the symptoms along with flu-like conditions that mark the HIV infection.
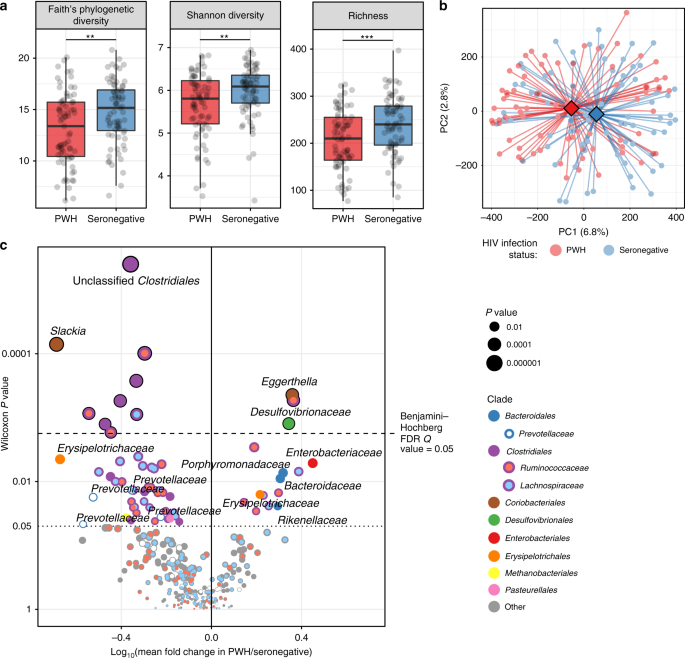




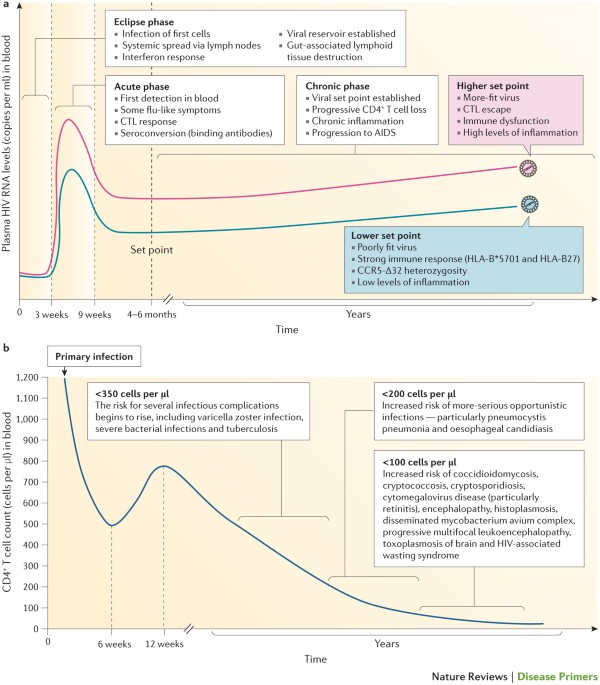
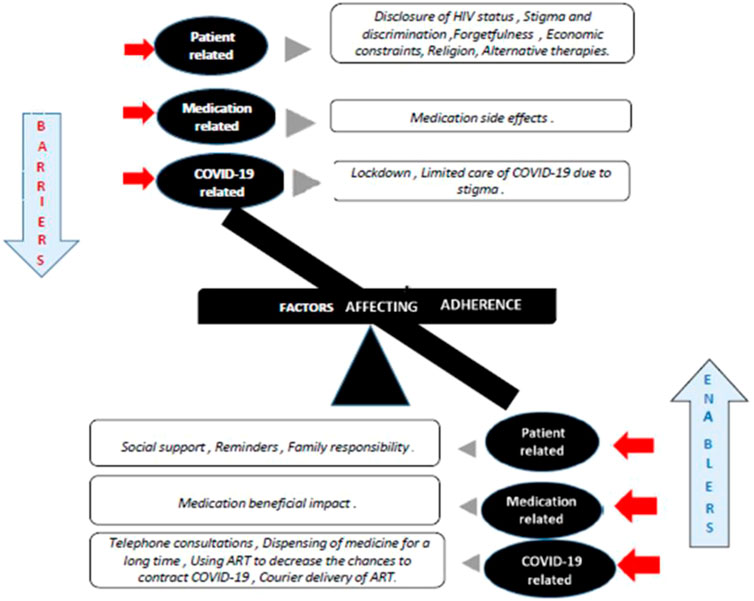


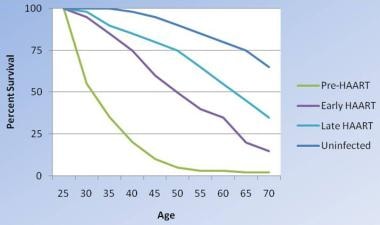
/Aids-and-autoimmune-diseases-5113376_final-f35eaa36335d4e4d8638ac86fdf16146.jpg)



/Aids-and-autoimmune-diseases-5113376_final-f35eaa36335d4e4d8638ac86fdf16146.jpg)














Post a Comment for "39 hiv and aids are different labels for the same disease"